Overcome Common Process Automation Challenges with Digital Q.BPM

April 8, 2024
Digital Q.BPM is a highload microservice-based bpm platform designed to effectively automate and streamline your business processes. Digital Q.BPM combines global BPM Best Practices enhanced with Diasoft’s vast expertise in the financial services market. It provides unique tools for automation of business processes and successfully implements complex multi-step processes – from process design to go-live.
Due to its unique features, Digital Q.BPM easily overcomes common process automation challenges and weaknesses of many popular BPM systems. Let us explore these tools and features in detail.
Digital Q.BPM Unique Features & Advantages
1. DESIGN CHALLENGES
Version management: During design of a business process, responsible business units make multiple corrections and improvements and need to be able to track all changes and process versions. It can be difficult to restore a specific version of the process, and this simple action can take a lot of time in common BPMS platforms.
- Digital Q.BPM maintains the history of process versions allowing developers to compare versions of visual process diagrams and track implemented changes.
Teamwork: In large companies, business processes are designed by large teams rather than dedicated experts, which requires management of the teamwork.
- Joint process design in DIGITAL Q.BPM allows several users to work together on the same business process diagram using a shared online whiteboard. Each user can see actions of other team members, while the system immediately implements all changes made by each user (not only the last one). Read more here.
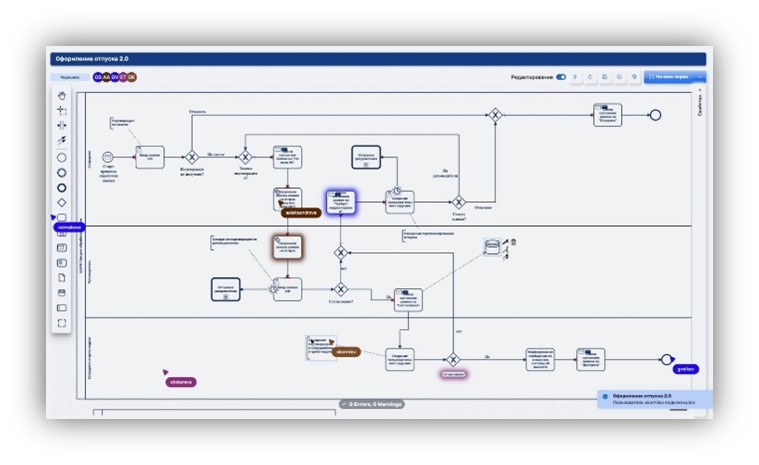
Flexible approval process: During the design process, technologists need to approve business processes, but standard BPM platforms either do not support the approval process or do not allow customizing it.
- Digital Q.BPM support a special process for approval of diagrams which can be customized to customer needs.
Reusable templates: When designing similar or same-type processes, users have to export an existing diagram and import it to a new one, or make a copy of the existing diagram.
- Digital Q.BPM supports not only copying, but also allows saving new diagrams as templates. Templates are used to easily design of new business functions. Ready templates are stored in the centralized register.
Documentation: 90% of BPM documentation can be understood only by an experienced user and refers to technical details of the process design.
- Digital Q.BPM is supported with the intuitive documentation which is easily understandable by both experts and inexperienced users. It describes all stages of process design and management, and comprises description of best practices, use cases and business process design patterns. Learn more here.
2. DEVELOPMENT & INTEGRATION CHALLENGES
Integration: Many BPM platforms do not support event-driven integration with external systems, which causes difficulties for full automation of business processes. The use of standard HTTP connectors in popular BPM systems makes it difficult to integrate business processes into the company IT landscape due to authorization issues.
- Synchronous interactions of IT systems are supported through the REST APIs, and asynchronous interactions use the message broker. The choice of the approach depends on system requirements and parameters, its response time, reliability and performance. Digital Q.BPM automatically creates Swagger contracts to start, stop and change the context of a business process. Each API refers to a specific process and runs format and logical control at the start of the process.
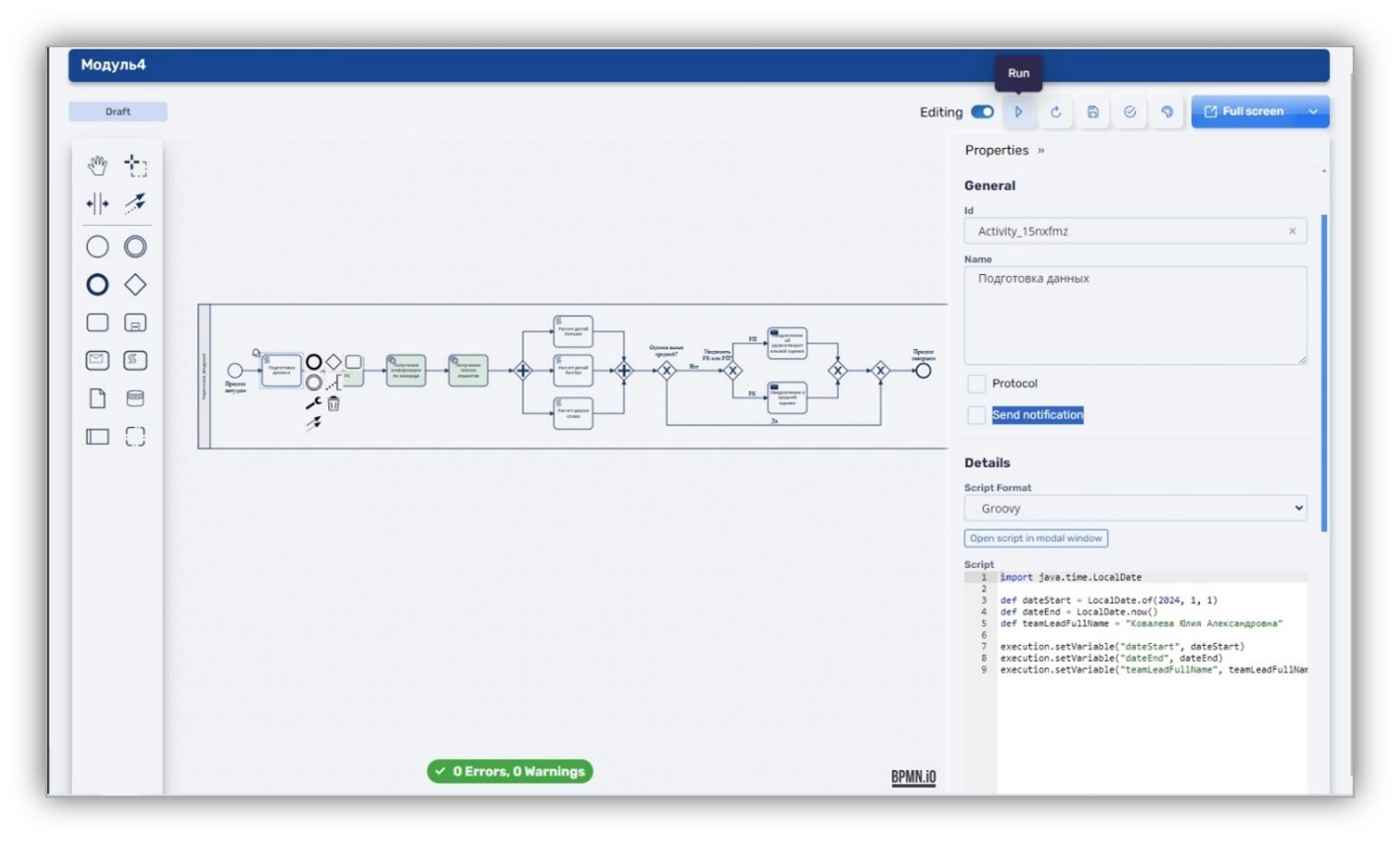
- Debugging tools: The lack of effective debugging tools slows down go-live of new business processes.
Advanced debugging tools in Digital Q.BPM allow starting processes immediately in the process designer. During debugging, the user can set up values of parameters and save the required number of test data for repeated start of the processes to check how they run in different versions. The platform supports step-by-step debugging.
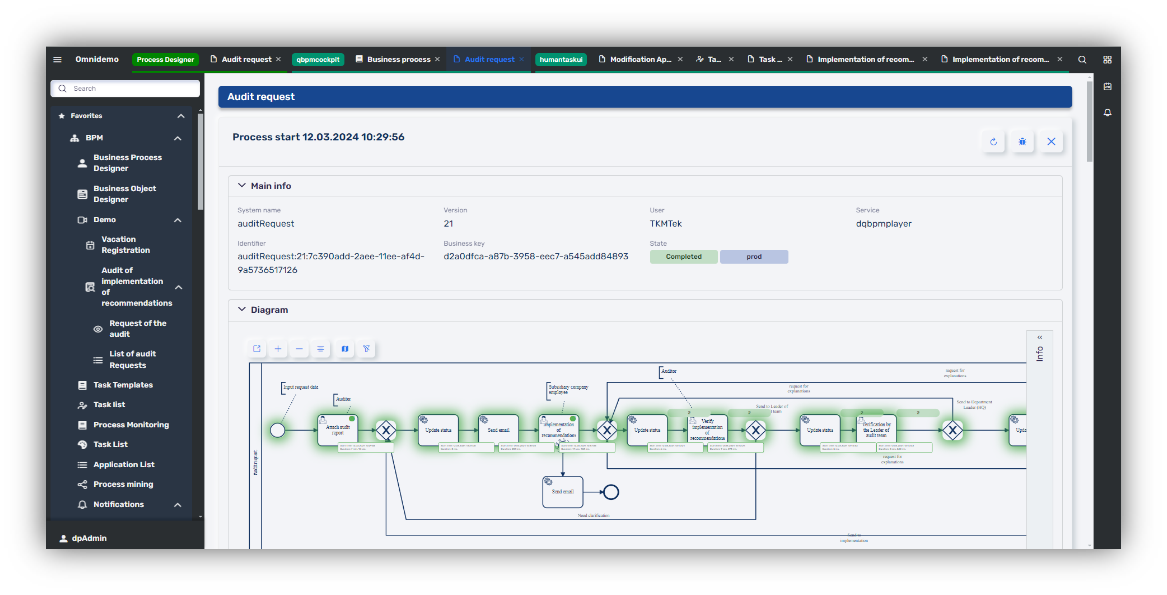
Testing: Without special analytical tools in the bpm platform, the analysis of the business process may be complicated and resource-intensive.
- Digital Q.BPM provides a powerful Monitoring System for the overall analysis of business processes. It allows easily checking if the process follows the planned logic during acceptance testing and find out the reasons in case of deviations.
Special Development Tools: Digital Q.BPM provides special plugins that facilitate the development process:
- Mini Map – Helps users to better navigate in a long process and quickly move to the specific part, find required objects and switch between objects.
- Global Search in Diagrams – Reduces time for the search for specific process parameters, helps to find all variables matching the search criteria. This feature facilitates search in large diagrams, events or integration flow requests, where the manual search is especially complicated and takes a lot of time.
- Token Simulation – Provides visual representation of process execution and allows users to visually identify potential issues in complex processes.
- Automatic Check for design errors and matching to the process notation.
3. GO-LIVE CHALLENGES
To track process versions and deploy the functionality in the production environment, Digital Q.BPM offers two options:
- Export and import of diagrams, with their further publication with the help of the platform tools.
- The use of DevOps pipeline, which ensures secure versioning and automatic delivery of edited processes to required environments.
Migration: When a new process version is deployed in the production environment, it is often challenging to migrate earlier launched processes to the newly published version. Even in technologically advanced BPM platforms, the migration cannot be done without involvement of business process developers who took part in the design of the process.
- Digital Q.BPM provides a special interface for process migration. The platform automatically creates the migration plan and defines the list of process instances to be migrated to the new version. With this approach, the involvement of the business process developer is needed only in about 5% cases.
4. SYSTEM USE & MAINTENANCE CHALLENGES
Monitoring tools: When the system runs multiple processes, it needs special tools to monitor correct and incorrect operation of services.
- Digital Q.BPM provides modern pre-integrated tools for monitoring and management of business processes. Even though different processes are executed in different microservices, the platform provides a centralized interface for their monitoring. All executed business processes are available in the same environment and are always at hand. Execution of each business process and business rule is presented visually – exactly in the same form as the diagram was designed.
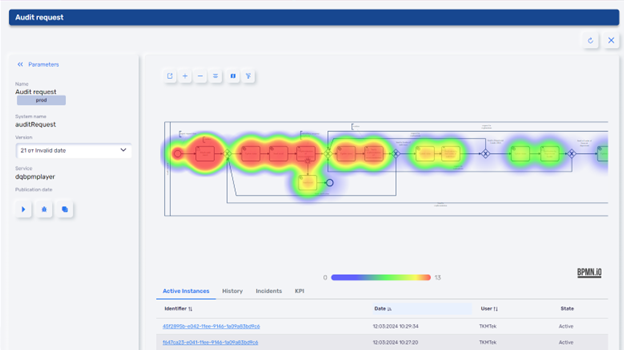
- HEAT MAP: Digital Q.BPM supports process analysis in different analytical dimensions. Heat maps allow for easy detection of process bottlenecks by execution time, frequency of execution of process blocks, amount of data used at different stages. Statistical monitoring collects information on the quality and speed of execution of business processes (the number of business processes currently run in the system, the number of executed business processes, the number of business processes executed with incidents, significant violations of KPIs, etc.).
Reliability and fault tolerance: Most BPM platforms with the monolithic architecture use centralized execution of all business processes. This approach significantly slows down the system in case of a large number of business processes and can cause limitations in fault tolerance, when a failure of one component can stop the entire system.
- To overcome restrictions of the monolithic architecture, Digital Q.BPM supports decentralized process execution in separate microservices. It improves the system reliability and fault tolerance, since the failure of one microservice does not stop other processes in the platform.
- The centralized management and monitoring of all microservices in Digital Q.BPM ensures a centralized representation of states and execution of all business processes. It facilitates process control, ensures centralized management of process parameters and settings, allows users to quickly respond to changes and system issues.
System performance and scaling: Support of the growing number of users and business processes often becomes challenging in traditional BPM platforms.
- Digital Q.BPM stores the history in the dedicated central data storage that does not influence execution of the business process, which improves the performance by 30–40%.
- The microservice architecture of Digital Q.BPM guarantees high flexibility, reliability, and efficient business processes management and monitoring in companies with a large number of business processes. The decentralized execution of business processes enables flexible horizontal and vertical scaling. Microservices can be scaled and developed independently, which enables more effective and flexible management of business processes, reduces Time-to-Market and streamlines the use of computation resources.
Learn more about Digital Q.BPM

